Hybrid VS. Electric Car: Which Has the Greatest Advantage?

Our world is changing. Change in and of itself is not necessarily bad or good, but rather a mix of the two.
Petroleum-fueled vehicles helped to drive the world into an era of globalization and togetherness that has never before been seen, but there are rising challengers that threaten to overtake the seemingly unshakeable king of automobiles . . . hybrids and electrics are rapidly becoming more affordable and more powerful, fighting back against the perception that any vehicle not powered entirely by oil is not a true car.
The Total Electric Vehicle
Despite climate change and dwindling fuel sources pushing electric vehicles into focus, we have had access to them for far longer than petroleum-fueled cars. In the 1830s, the first electric vehicles came into existence thanks to the independent efforts of American blacksmith Thomas Davenport and Scottish engineer Robert Anderson. Until the development of Henry Ford’s manufacturing technique in the 1900s decreased the cost of gasoline driven cars to a third of the price of the conventional electric vehicle of the time, people elected to drive an electric vehicle overwhelmingly over any other option.
How Do Electric Cars Work?
Under the hood, the electric vehicle uses stored electrons to drive the motor and spur the hunk of metal into motion. Early battery technology gave the cars limited range, but electrics were still the go-to for drivers due to their ease of use and lack of noxious fumes. Now, the leading electric car can go almost 300 miles on a full charge, providing comparable performance to the energy density of a full tank of gasoline. The inner workings of an electric car are also free from having to manage a never-ending series of small explosions, and the maintenance costs of the electrics are understandably lower than their peers.
The Battery-Run Hybrid
 Although electric vehicles could be seen as the first true automobiles, hybrids that combine the power of gasoline and electricity for locomotion are a more modern invention. Beginning in the 1990s, increasing fuel prices and concerns over climate change began to spur development into alternative fuel sources. Even “gasoline-fueled” vehicles use small amounts of electricity for powering equipment, but a hybrid electric vehicle will more specifically use electrical energy to push itself into motion. The petroleum powered portions of the automobile activate as needed for greater bursts of speed, filling the gaps in energy production, and working with the electrical portions to provide smooth acceleration throughout the trip and eliminate the need for engine idling.
Although electric vehicles could be seen as the first true automobiles, hybrids that combine the power of gasoline and electricity for locomotion are a more modern invention. Beginning in the 1990s, increasing fuel prices and concerns over climate change began to spur development into alternative fuel sources. Even “gasoline-fueled” vehicles use small amounts of electricity for powering equipment, but a hybrid electric vehicle will more specifically use electrical energy to push itself into motion. The petroleum powered portions of the automobile activate as needed for greater bursts of speed, filling the gaps in energy production, and working with the electrical portions to provide smooth acceleration throughout the trip and eliminate the need for engine idling.
How Do Hybrid Cars Work?
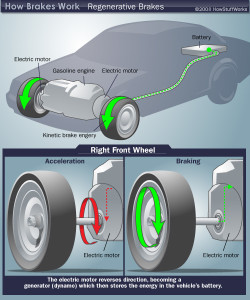
The key difference that the everyday user of a hybrid will note compared to electrics is how you refuel. Hybrids use a technique called regenerative braking to produce electricity from the force of the car stopping, so the driver only has to refill the gasoline tank, In fact, most hybrids do not have a way to connect with an outside power grid.
What Does an Electric Vehicle Service Technician Do Differently?
When working with electric and hybrid vehicles, the technician requires a greater depth of knowledge about the differing systems in each automobile. Just like switching between two models of gasoline vehicles, every electric and hybrid will have its own configuration and specifications that have to be considered. Typically, the differences are relegated to the engine block and drive train for electric vehicles, with many notable parts essential for hybrid and gasoline vehicles being removed entirely. These include the fuel injection system, alternators, the typical car battery, radiator, and potentially much more depending on the model.
The Future of Automobiles
With the renewed interest shown in preserving the planet through reducing consumption combined with improvements in technology enhancing their performance, electric vehicles of all types have been seeing a greater share of market movement. There were under 50,000 electric vehicles sold in 1990, but that number has increased more than eight times since then.
For an automotive service technician, it is incredibly prurient to acquire as much experience and knowledge about electric, hybrid, and petroleum-fueled vehicles. A proper breadth of information will allow the AST to maintain a diverse fleet of automobiles and improve their value to their shop. The mechanic will need experience with both the mechanical aspects and the electronic aspects of every vehicle that rolls in for repairs.
The ceremony is about to begin! #ATI #ATIGRAD pic.twitter.com/8SJb0Nb02L
— ATI (@AdvTechInst) August 14, 2015
Want to Learn to Work on Hybrid and Electric Vehicles?
If you dream of a career where you get to delve into the inner workings of powerful pieces of engineering, consider enrolling in the Automotive Technology with Service Management (AOS) program at ATI. You could learn how to diagnose, repair, and maintain the mechanical and electronic systems found on modern vehicles and will take steps towards a fulfilling life that rewards you properly for your hard work and effort. Contact us at 800-468-1093 or request information on our website today.
DISCLAIMER – Advanced Technology Institute (ATI) makes no claim, warranty or guarantee as to actual employability or earning potential to current, past or future students or graduates of any educational program offered. The Advanced Technology Institute website is published for informational purposes only. Every effort is made to ensure the accuracy of information contained on the AUTO.edu domain; however, no warranty of accuracy is made. No contractual rights, either expressed or implied, are created by its content.
Gainful Employment Information – Automotive Technology with Service Management (AOS)
Gainful Employment Information – Automotive/Diesel Technology
For more information about Advanced Technology Institute or any of our programs click here: http://www.auto.edu/ or http://ow.ly/VoydP.
Industry Knowledge
Welcome to the Advanced Technology Institute's Blog, your resource for industry insights and discussions on technologies shaping the future of automotive, heavy vehicle, hvac, welding, and other related career paths.
Explore how ATI's curriculum and hands-on learning opportunities can propel your career in the tech-driven world.






